Key Takeaways
- World Mental Health Day is October 10th a day to raise mental health awareness
- As a physiotherapist, you primarily focus on physical rehabilitation, but you also know mental health plays an important role in recovery
- There are many adverse psychological reactions that can occur when patients can no longer do daily tasks and hobbies that they enjoy
- Learn what symptoms are warning signs that your patient will require additional mental support during rehab
- Find out 6 ways you can support your patients’ mental health
Every October 10th it’s World Mental Health Day: a day to raise awareness of mental health issues around the world and to mobilise efforts in support of mental health.
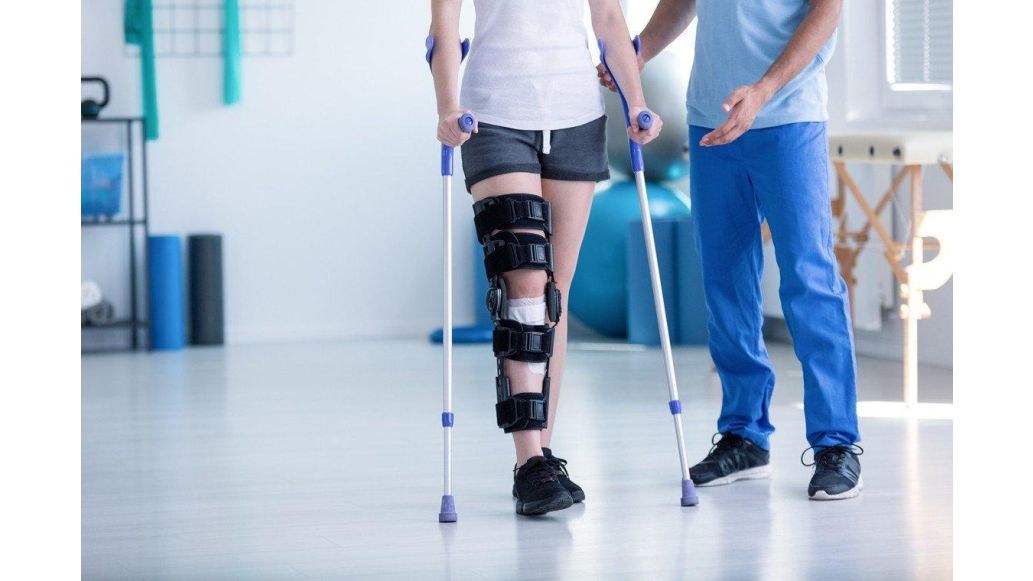
Rehabilitation is usually thought of as the physical activities that heal and optimise the musculoskeletal system, but as a physiotherapist, you know that mental health also plays a big role in patient recovery.
Learn more about the important role mental health plays in the post-injury phase. We're honoring World Mental Health Day by covering the ways in which you can help your patients stay positive and engaged to increase their recovery outcomes!
- Adverse Post-Injury Psychological Reactions
- How Mental Health Can Impact Injury Rehabilitation
- 6 Ways to Support Your Patients’ Mental Health

Adverse Post-Injury Psychological Reactions
Whether it’s a broken knee or spinal trauma, injuries change a patient’s life and routine drastically. Reactions to this interruption in the daily norm will vary from person to person depending on personality and psychological factors, but you should prepare your patients to handle this transition. For example, patients who can no longer participate in activities that bring them joy or stress relief like sports can experience frustration and sadness. People who can no longer be as socially active as they once were may experience feelings of isolation. People who are not able to continue working may feel a lack of purpose or loss of identity. Other emotional responses to include: 1
- Irritation
- Denial
- Guilt
- Anger
- Withdrawal
- Anxiety
- Disengagement
- Depression
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Problematic emotional reactions occur when symptoms do not resolve or worsen over time, or the severity of the symptoms seems excessive relative to other patients.1 If your patient is exhibiting any of the warning signs in the table below, he or she will require additional psychological support throughout the rehabilitation journey.
PROBLEMATIC EMOTIONAL REACTIONS (EXAMPLES):
Persistent Symptoms
- Alterations of appetite
- Sleep disturbance
- Irritability
Worsening Symptoms
- Alterations of appetite into disordered eating
- Sadness into depression
- Lack of motivation into apathy
- Disengagement into alienation
Excessive Symptoms
- Pain behaviors
- Excessive anger or rage
- Frequent crying or emotional outbursts
- Substance abuse

How Mental Health Can Impact Injury Rehabilitation
Even if your patients have the physical ability to do their rehabilitation programs, they need their mental health to complete it to the best of their ability. While you’re monitoring for the signs of psychological distress, be on the lookout for some ways in which emotional decline can be impacting your patients’ outcomes, like:
Lack of Motivation
If your patients are experiencing emotions like sadness, frustration, or withdrawal, feelings of hopelessness can keep them from staying faithful to their rehab. This can also stem from the rehabilitation timeline; while injuries like an ACL tear have a somewhat predictable timeline for rehab and recovery, the timeline for an injury like a concussion is generally unknown.2 Without a promised date they can return to activity and their daily routines, patients will find it difficult to stay motivated.
Fear of Re-injury
Post-injury, it’s natural for patients to play the incident back in their heads to analyse the situation, figure out what went wrong, and decide how to avoid it next time. Unfortunately, for patients experiencing problematic emotional reactions, this activity can create further fear and cause an unhealthy level over overthinking. To identify patients with fear of re-injury, be on the lookout for hesitation, uncertainty, and potential emotional outbursts during rehabilitation.
Persistent Denial
Denial can manifest in a few ways during the rehabilitation process, but one of the most common is denial of injury severity.1 Patients’ emotions may compel them to think that the injury isn’t as bad as healthcare professionals say it is, or the recovery process you’ve created doesn’t apply to them. In these situations, a mixture of emotion and ego can cause patients to skip rehabilitation and disobey limitations set by clinicians.
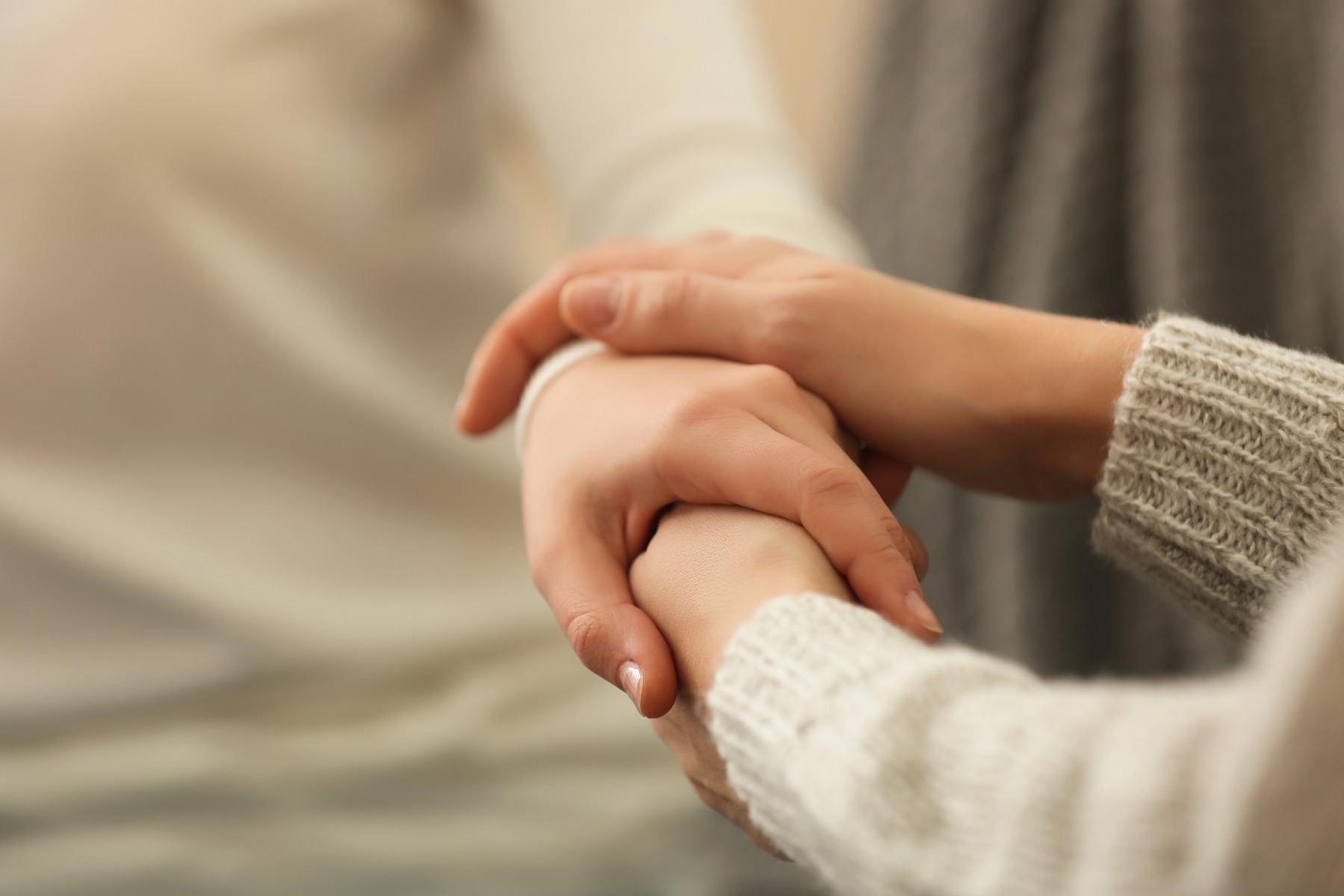

6 Ways to Support Your Patients’ Mental Health
If you want to enhance your patient’s psychological wellbeing to help them through rehab, here are six methods you can try with every single patient:
- Educate. The more your patients understand their injury and the recovery process, the more equipped they will be to overcome it. Make sure you present the information in a way that the patient will understand and dispel any misinformation the patient may have read on the internet or heard from others.
- Build trust. Injured patients can experience a range of emotions that make it difficult for care network members to establish rapport. Listening to your patients is particularly important, not only to make a medical diagnosis but also to assess and monitor their emotional state.1
- Set goals. If the patients have periodic, measurable goals to achieve, they may be more motivated and enthusiastic to complete their rehabilitation.
- Create a network. Your patients are only with you a certain amount of hours a week. Who’s going to be there for them when you’re not there? Help your patients build a social support system with family, friends, colleagues, and peers.
- Seek additional help. As qualified as you are to take your patients through the rehabilitation process, your skills can only go so far. Be sure to have a qualified mental health specialist ready for referrals if your patients need additional psychological support.
- Try stress coping skills. Injured athletes can experience considerable stress throughout the injury and rehabilitation process. Psychological and physical strategies will enhance the recovery process.1
SELECTED TECHNIQUES FOR COPING WITH STRESS:
Cognitive-Based Techniques
- Thought stopping
- Thought replacement and imagery
- Positive self-talk
Somatic-Based Techniques
- Slow, deep or centered breathing,
- Progressive muscle relaxation
- Biofeedback training
Cognitive Behavioral-Techniques
- Goal setting
- Stress management training
Thank You From Performance Health
To all of the dedicated hands-on healthcare professionals who dedicate your lives to helping others heal, we thank you and support you! We appreciate how you focus on your patients’ physical and mental well-being not only on World Mental Health Day, but year-round. Thank you!
References
- American Academy of Family Physicians, American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, American College of Sports Medicine, American Medical Society for Sports Medicine, American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine, and the American Osteopathic Academy of Sports Medicine. (n.d.). PSYCHOLOGICAL ISSUES RELATED TO INJURY IN ATHLETES AND THE TEAM PHYSICIAN: A CONSENSUS STATEMENT. American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine. Retrieved from https://bit.ly/39CJ6C2
- Putukian, M. (n.d.). Mind, Body and Sport: How being injured affects mental health. NCAA Sports Science Institute. Retrieved from https://bit.ly/2PMhKT7
Medical Disclaimer: The information provided on this site, including text, graphics, images and other material, are for informational purposes only and are not intended to substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other healthcare professional with any questions or concerns you may have regarding your condition.






 US
US France
France Australia
Australia