Causes and Treatment for Peripheral Neuropathy
In the United Kingdom, an estimated one in ten people over the age of 55 suffer from some type of peripheral neuropathy.1 Peripheral neuropathy is a condition created by the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord, known as the peripheral nervous system. Nerve damage can be caused by physical trauma, exposure to toxins or chemicals, or certain medical conditions including cancer, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. In this article, we will break down what causes peripheral neuropathy and ways to treat and manage symptoms.
Key Takeaways
- One in ten people over the age of 55 in the UK suffer from some type of peripheral neuropathy.
- Peripheral neuropathy is often caused by nerve damage and impacts the nervous system.
- Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy are rarely life-threatening and often can be managed with proper treatment.
Table of Contents
Diagnosis: What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
Most Causes Common of Peripheral Neuropathy
Treatments for Peripheral Neuropathy
Managing Peripheral Neuropathy at Home
Conclusion
Top Products in This Article
Diagnosis: What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
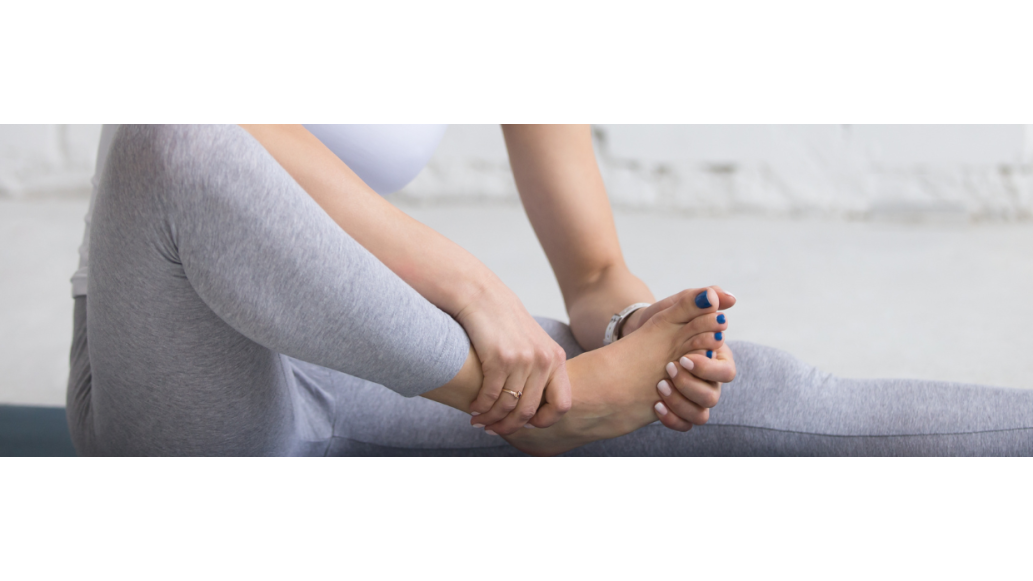
Peripheral neuropathy, often caused by nerve damage, impacts the nervous system, which helps send signals between the central nervous system and our entire body. The damage can often cause muscle weakness, known as motor nerve damage.2 In some cases, it can cause sensory nerve damage. This can look different on every person, as sensory nerves have many different functions. For example, in diabetics, a common symptom is a loss of feeling in one's feet, or a painful stinging feeling. For others, peripheral neuropathy can cause full loss of feeling in a limb or extreme pain by something such as a bed sheet touching the skin.
Peripheral neuropathy symptoms vary due to nerve signaling being disrupted in three different ways.2 These ways include loss of how signals are normally sent (think of a broken wire), signaling when there shouldn’t be (static while on a phone), or by errors that distort the messaging (a fuzzy TV picture during a storm). Since there are separate ways nerve signaling can be impacted, symptoms can range from mild to disabling, but are hardly ever life-threatening.
Most Common Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy
- Diabetes
In the UK, diabetes is the number one cause of peripheral neuropathy.1 It is also the number one cause of non-traumatic lower limb amputations in the country. However, if the symptoms are noticed earlier, amputations can be prevented. In fact, 75% of amputations caused by diabetic peripheral neuropathy are preventable.
- Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is hard on the nervous system since nerve cells are more sensitive than other cells in the human body.1 Some chemotherapy drugs can cause symptoms of peripheral neuropathy during or right after the first dose, while others can have delayed symptoms.
- Idiopathic
In these cases, there is no specific cause that makes peripheral neuropathy appear.1 When there is no specific cause, peripheral neuropathy is considered the primary disease. This typically happens in middle-aged and elderly individuals. An estimated 23% of patients are given this type of diagnosis.
- HIV or AIDS
Statistically, 1/3 of HIV or AIDS patients will have peripheral neuropathic conditions as well.3 This is due to side effects in certain medications used to treat HIV and AIDs. In cases where the medication for HIV or AIDS causes symptoms of peripheral neuropathy, it can be treated by stopping usage of the drug or reducing the dosage used.
Treatments for Peripheral Neuropathy
While there are a variety of ways to treat peripheral neuropathy, some are more common. In some cases, as mentioned above, this could just mean refraining from taking the drug that is causing peripheral neuropathy as a side effect. However, in other cases, additional tests may be needed to help determine the extent of the disease.
A physiological test can be done to help determine nerve function.2 Options like Nerve Conduction Velocity tests measure the strength and speed of nerves, where Electromyography (EMG) tests involve inserting needles into muscles to record their activity. EMG tests can help determine responsiveness, irritability, and help detect abnormal muscle electrical activity. Other test options might be a nerve biopsy to examine the nerve tissue, or a radiology imaging test, such as a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
After determining the extent of the disease, treatments can be prescribed. Often, physical therapy will be prescribed. Research shows exercises done regularly can reduce the pain from peripheral neuropathy and help improve muscle strength.4 Some common exercise examples can be found below.
- Aerobic Exercise– a walk on the treadmill or water aerobics can help get the body moving. Using a stationary bicycle is another option for this type of treatment.
- Flexibility Exercise– Calf stretches or the seated hamstring stretch are great ways to help keep joints flexible.
- Strength Training Exercise– Chair squats or calf raises can help make muscles stronger, and in turn reduce the chance of injury.
- Balance ExerciseTraining with single leg balances and side leg raises can help with the feeling of unsteadiness due to nerve damage. These exercises can also help with joint pain and weakness, so patients are less vulnerable to falls.
Managing Peripheral Neuropathy
There are many ways patients can manage their diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Below are a variety of solutions to offer your patients.
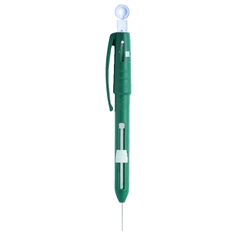
1. Neuropen Kit
A dual function-screening device, the monofilament test enables the clinician to map areas of reduced pressure perception by exerting a specific repeatable force on the test site. Using a Neurotip within a Neuropen ensures that a quantifiable force can be exerted safely onto the skin to identify a patient's decrease in sensation to sharpness.
2. Sorbothane Cush N Step
This insole is perfect for someone dealing with a hypersensitive or diabetic foot. By dispersing shockwaves laterally, this insole can play a significant role in your patients’ orthotic treatment regimen.
3. Jamar Monofilaments
Monofilaments are used as a foot screening tool to help detect early sensory loss in neuropathic and amputation risk patients. The monofilaments are designed for easy touch motion to detect sensory loss on the foot.
4. GEHWOL med Salve for Cracked Skin
A great moisturizer, GEHWOL med Salve for Cracked SkinEucerin Daily Lotion nourishes and repairs dry skin. A dermatologically tested brand, the product protects the skin and allows it to regain its natural elasticity and resilience.
Conclusion
Peripheral neuropathy impacts thousands of people in the UK. The causes of peripheral neuropathy can range from autoimmune diseases to herbicide exposure, chemotherapy, and diabetes. While it can be cured on its own in some cases, there are treatment options for patients experiencing discomfort. Performance Health can help support your clinic’s supply needs to enable positive patient outcomes and lower the chances of a costly readmission.
Resources
- NHS website. (2022, October 12). Peripheral neuropathy. Nhs.uk. https://bit.ly/3W28HL7
- Peripheral Neuropathy Fact Sheet | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. (n.d.). http://bit.ly/3OMWTto
- Foundation for Peripheral Neuropathy. (2022, November 10). HIV/AIDS. The Foundation for Peripheral Neuropathy. http://bit.ly/3Uj11Cr
- Foundation for Peripheral Neuropathy. (2022a, November 9). Exercises For Peripheral Neuropathy - Physical Therapy. The Foundation for Peripheral Neuropathy. https://bit.ly/3Vjej3l
Medical Disclaimer: The information provided on this site, including text, graphics, images, and other material are for informational purposes only and are not intended to substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other healthcare professional with any questions or concerns you may have regarding your condition.






 US
US France
France Australia
Australia